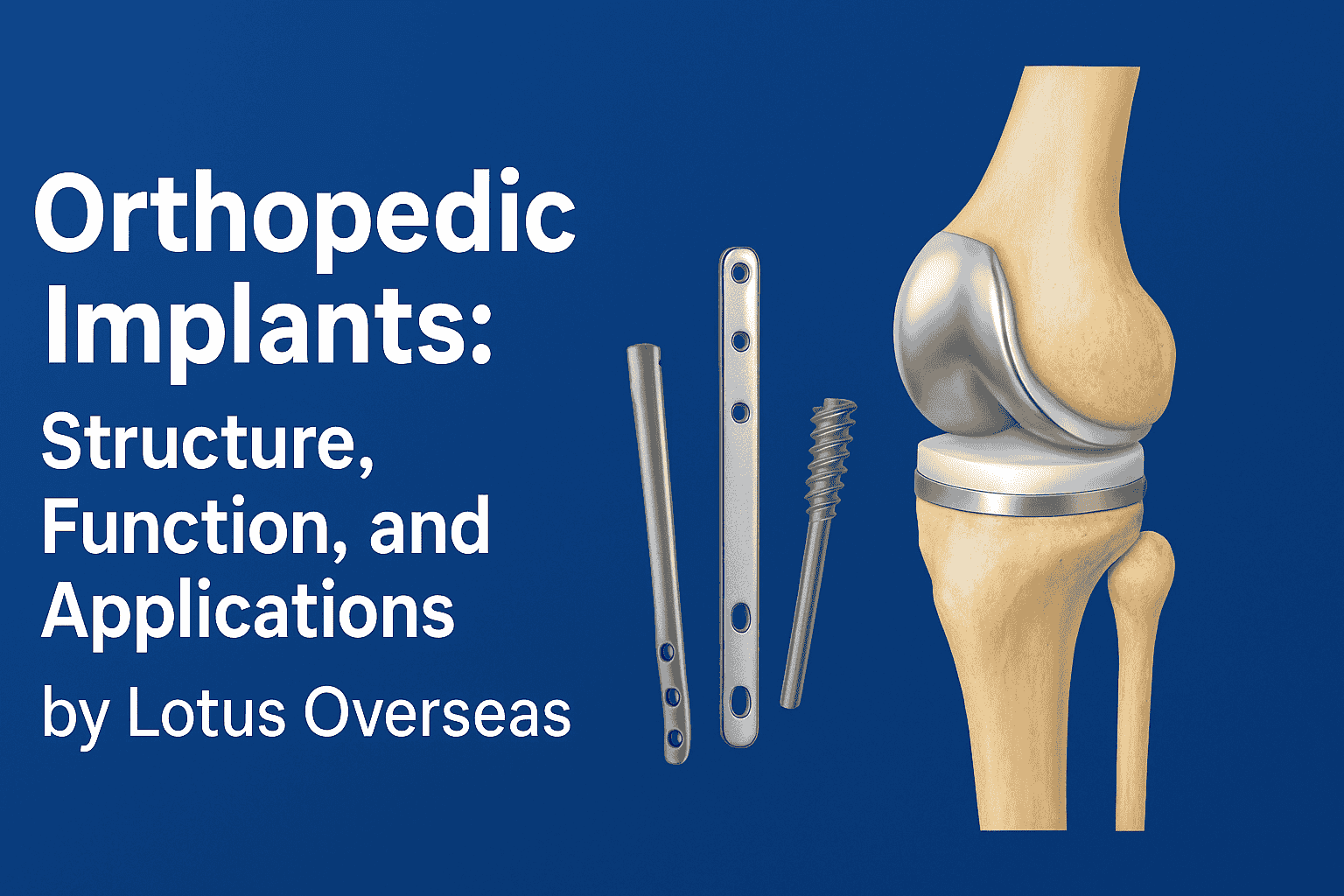
Orthopedic implants are essential medical devices that restore function and stability to damaged bones and joints. They help patients regain movement after trauma, deformities, or degenerative diseases. Orthopedic implants are used in surgical procedures across trauma care, spine correction, and joint replacement. Each implant type is designed with specific mechanical properties to match the anatomy and movement of human bones.
Lotus Overseas manufactures orthopedic implants with a focus on structural accuracy and material safety. The company follows international standards in every step, from design and machining to finishing and sterilization. Orthopedic implants must perform reliably under stress, which demands precise engineering and testing. Understanding how these implants work helps medical professionals and patients make informed decisions about their use.
What Orthopedic Implants AreOrthopedic implants are medical devices inserted into the body to replace or support bones or joints. They help stabilize fractures, correct deformities, and restore mobility. Most implants are made from stainless steel, titanium, or cobalt-chrome alloys. These materials resist corrosion and have mechanical strength similar to natural bone. Their biocompatibility ensures that body tissues accept the implant without causing an immune reaction.
Orthopedic implants include several main categories:
Bone plates: Flat or contoured metal pieces fixed with screws to hold fractured bone segments in alignment.
Bone screws: Threaded fasteners that secure plates or directly anchor bones during healing.
Intramedullary nails: Long metal rods placed inside the bone marrow cavity to stabilize long bone fractures such as the femur, tibia, or humerus.
Joint implants: Artificial replacements for damaged joints, including hips, knees, and shoulders.
Spinal implants: Rods, cages, and screws that support and stabilize the vertebral column.
Each implant type performs a defined mechanical function. The choice depends on the bone location, fracture pattern, and load-bearing requirement.
Material Selection in Orthopedic ImplantsMaterial choice is one of the most critical aspects of implant design. Each metal or alloy used in orthopedic implants must meet specific requirements for strength, fatigue resistance, and corrosion control.
Stainless steel (316L): Commonly used for trauma implants such as plates and screws. It provides strength and ductility, allowing surgeons to contour it during surgery.
Titanium and titanium alloys: Used for long-term implants and joint replacements. Titanium is lightweight and has high corrosion resistance. It bonds well with bone through a process called osseointegration.
Cobalt-chrome alloys: Known for hardness and wear resistance. They are used in load-bearing joints such as the hip and knee.
The surface finish of an implant affects its performance. Smooth surfaces reduce tissue irritation and friction, while rough or porous surfaces support bone growth. Polishing, coating, and texturing are controlled steps during manufacturing. Lotus Overseas applies strict inspection at each stage to ensure consistency.
Design and Manufacturing StandardsOrthopedic implants must follow international quality and safety standards. These include ISO 13485 for medical device quality management and CE certification for European compliance. Each implant undergoes dimensional verification, material testing, and sterilization validation before shipment.
Design accuracy is vital. Even a minor deviation can affect how the implant fits in the body. Computer-aided design (CAD) and computer-aided manufacturing (CAM) systems help ensure precision. Lotus Overseas uses automated machining tools and inspection equipment to achieve accurate geometries and surface finishes.
Every implant passes through multiple quality checks. Visual inspection, hardness testing, and fatigue testing confirm structural integrity. Sterile packaging ensures implants remain free from contamination until use.
Applications of Orthopedic ImplantsOrthopedic implants are used in several medical fields:
Trauma Surgery
Fixation of bone fractures with plates, screws, and nails.
Common in accident and injury cases.
Implants help maintain alignment during bone healing.
Joint Replacement
Replacement of worn-out or damaged joints with artificial components.
Used mainly for hip, knee, and shoulder joints.
Improves patient mobility and reduces pain.
Spinal Surgery
Correction of spinal deformities or stabilization after injury.
Uses rods, screws, and cages to support vertebrae.
Reconstructive Surgery
Used after tumor removal or severe deformity correction.
Custom-designed implants may be required for complex cases.
Each surgical application demands implants with specific properties, such as strength, flexibility, and fatigue resistance.
Surgical ConsiderationsSuccessful orthopedic surgery depends on accurate implant selection and placement. Surgeons evaluate bone density, fracture type, and patient activity level before choosing the implant. Proper alignment is critical for healing. Incorrect implant size or placement can lead to complications such as non-union or implant failure.
Lotus Overseas manufactures implants in a wide range of sizes and geometries to accommodate various anatomical structures. Consistent dimensions help surgeons select implants that fit precisely and reduce surgical time.
Sterility is another vital factor. Every implant must be sterile at the time of use to prevent infection. Implants are packaged under cleanroom conditions and sterilized using validated methods.
Maintenance and LongevityOrthopedic implants are designed to last for years inside the body. Longevity depends on several factors, including material type, patient age, physical activity, and bone health. Joint replacement implants can function effectively for 15 to 20 years when properly positioned and maintained.
For trauma implants, removal may be necessary once the bone heals completely. Surgeons assess the healing progress through imaging studies and decide whether to remove the implant. Some materials, like titanium, are left inside permanently due to their compatibility with the body.
Common Issues and DevelopmentsWhile orthopedic implants have improved over the years, certain complications still occur. These include infection, implant loosening, and wear of moving parts. Continuous research aims to improve materials and surface treatments to reduce these risks.
Recent developments include:
Porous coatings to encourage bone growth into the implant.
Antibacterial surface treatments to reduce post-surgical infections.
Computer-assisted surgical systems for better alignment.
3D printing technology for customized implants.
Such advancements support better clinical outcomes and faster recovery times.
Global Use and Market TrendsThe demand for orthopedic implants continues to increase worldwide. Factors include rising traffic accidents, sports injuries, and aging populations. According to healthcare data, fracture fixation procedures are growing rapidly in developing countries. The need for affordable and standardized implants drives growth in manufacturing hubs such as India.
India has become a major supplier of orthopedic implants due to its advanced production capabilities and adherence to global standards. Lotus Overseas contributes to this growth by supplying high-quality implants to hospitals and distributors. The company’s products support surgeons across multiple continents.
Regulations and ComplianceOrthopedic implants are regulated as medical devices. Each product must comply with regulatory standards such as ISO, CE, or FDA depending on the market. Compliance ensures that implants meet required safety and performance parameters.
Manufacturers maintain documentation for traceability and quality audits. Any nonconformance is analyzed and corrected through documented procedures. Continuous improvement systems ensure consistent product quality over time.
Lotus Overseas follows a structured quality management system to meet these global regulatory demands. This ensures safety, consistency, and accountability in every batch.
Training and EducationUnderstanding orthopedic implants requires technical training. Surgeons, technicians, and biomedical engineers must know the principles of biomechanics and implant design. Training programs teach how to select, handle, and implant devices properly.
Lotus Overseas supports education by providing technical data and usage guidelines to healthcare professionals. Proper training helps reduce surgical errors and improves patient outcomes.
Why Knowledge of Orthopedic Implants MattersIf you work in healthcare or biomedical engineering, knowledge of orthopedic implants helps you make informed decisions. Understanding the difference between implant types, materials, and designs allows you to select the correct solution for each case. Awareness of manufacturing standards ensures confidence in product safety.
You should learn how implants behave under mechanical stress, how they interact with bone tissue, and how surface treatments affect healing. This knowledge supports better collaboration between surgeons and manufacturers.
ConclusionOrthopedic implants are essential for restoring movement and stability in damaged bones and joints. Their success depends on design accuracy, material quality, and surgical technique. Companies like Lotus Overseas contribute to the medical field through consistent manufacturing, compliance with international standards, and technical support for healthcare professionals.
Every implant produced under these standards represents precision, safety, and engineering discipline. Understanding orthopedic implants helps medical professionals improve surgical outcomes and patient recovery across the world.
You may also like
More from this category.

The Power of Tandoor Ovens in Modern Commercial Kitchens
Tooth Extraction in West Delhi – Expert Oral Surgery Care | DentoHub

Vinny Pizza: A Slice of Authentic Flavor with a Modern Twist

County Pizza: Where Local Flavor Meets Legendary Taste
NextGen Diagnostic Imaging

Get the Perfect Smile with the Best Orthodontist in Langar House at FMS Dental

Best Dentist in Hyderabad – Patient-Focused Care at FMS Dental

Why Selenium Is the Most Popular Tool for Web Automation?
Anti-Aging Treatments: Modern Solutions for Youthful, Healthy-Looking Skin

