As we know, the human implantation is the last barrier in the assisted reproductive technologies and this has been aptly spoken by Professor Bob Edwards himself. And as we know, there are two major points, there are two major actors in implantation, which are the uterus, that is the endometrium, and the embryo, which is the presenting part of the trophectoderm.
We know that both need to be adequately opposed and they both need to engage in a dialogue in order to have a successful implantation. So, there are various autocrine, paracrine, as well as endocrine factors that regulate the process of implantation. We have the autocrine factors that secrete locally and they are for the regulation and of the growth and differentiation of the endometrium, as well as the embryo, embryonic cells.
Paracrine factors from the reproductive tag, which are secreted under the influence of oestrogen and progesterone, that are again very, very important as far as the process of implantation is concerned. Although we do not have an accurate estimation of the implantation window, it has been estimated to last from day 20 to day 24 of the cycle, which amounts to about 72 to maximum 96 hours. After 2-3 days of the egg's fertilisation, embryo, still at the cleavage or morula stage, enters the uterus.
And at this stage, when it's still undergoing differentiation into the blastocyst stage, is when the process of implantation is known to occur. So, as we know, the progesterone induces the formation of pianofortes on the luminary surface of the endometrium and these pianofortes are then responsible for absorbing extra fluid from the endometrial cavity, forcing the blastocyst to oppose onto the endometrial surface. Blastocysts are known to prefer the sites which have the maximum pianofortes. This process is well explained with our hybrid Fellowship in Reproductive Medicine in India.
So, pianofortes are often considered as a positive sign for collaborating successful implantation. Implantation, by definition, is the process by which the embryo at the blastocyst stage comes into intimate physical and physiological contact with the endometrium and burrows inside itself and establishes itself into a pregnant. It is divided into three parts, apposition, adhesion and invasion.
As we go through the process of implantation, we know that the endometrium chlorophyllases under the estrogenic environment and it divides into multiple layers of epithelial cells. The endometrium is very active both as far as the celiac activity is concerned, the motility, also as far as the local secretion of substances like paracrine and autocrine factors are concerned.
So, we have the highly chlorophyllase endometrium that looks a triple layered in appearance on the ultrasound, which has a good vascularity also. There we have endometrium, which is conducive for the embryo to implant itself. After the estrogenic action of the endometrium, the progesterone acts on the endometrial cells and it leads to endometrial differentiation into secretory endometrium.
Histologically, we can observe that the endometrium's multilayered appearance is further differentiated into a progestogenic endometrium, which has several gland openings. The glands in question are in charge of secreting glycogen, a crucial nutritional substrate for the developing fetus. At this point, the blastocyst enters the uterus through the ostea and, in response to signals from different chemicals, rolls freely across the endometrium
One of them is L-selectin. Mucin I is another such a very important factor that repels the blastocyst. It repels the blastocyst from places which are not conducive to successful nidation.
It attracts the embryo to better locations by repelling the blastocyst and preventing its addition to endometrial regions with low implantation possibilities. The blastocyst is drawn to the ideal implantation location by chemokines and cytokines, which guarantees that an implantation not only proceeds successfully but also provides the optimum conditions for the embryo to thrive. To further guarantee successful implantation, other molecules such as integrins and catherines securely connect the blastocyst to the endometrial pinna board.
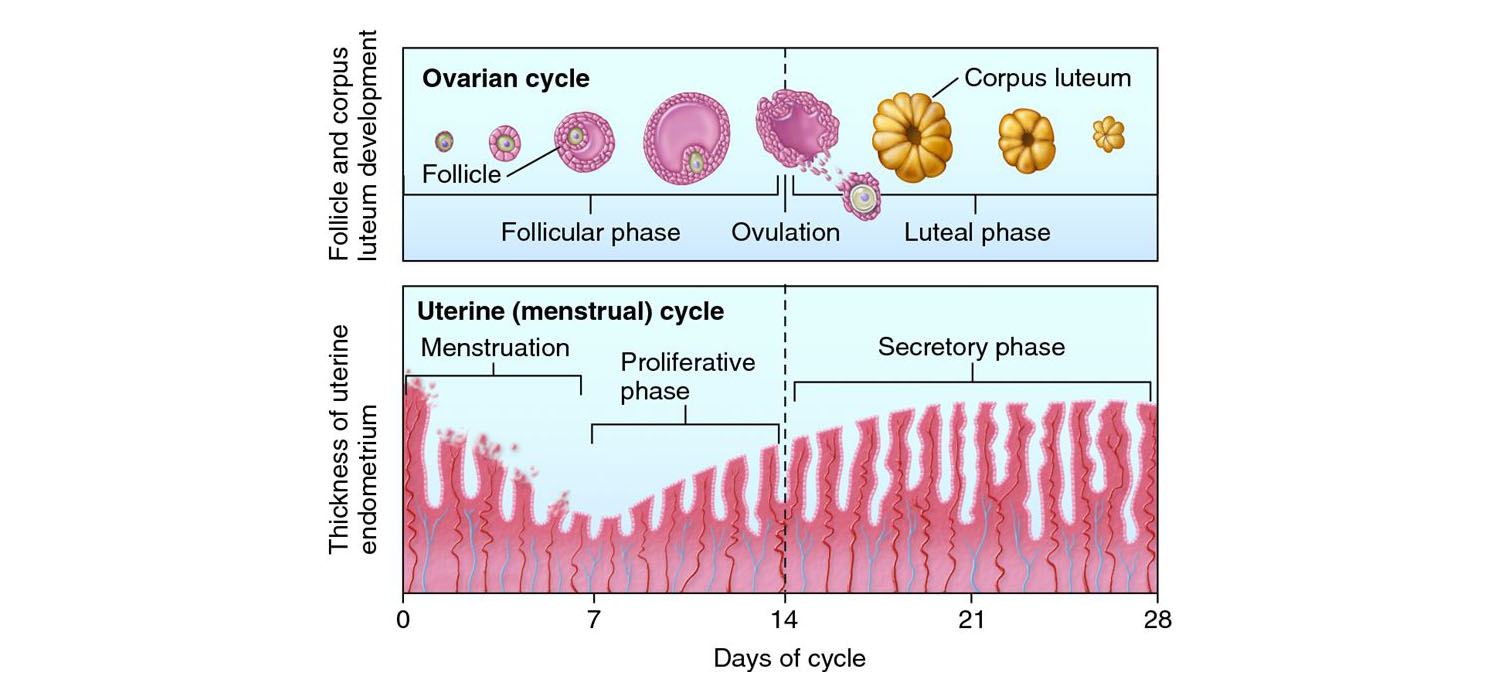
Here we have the endometrial remodelling in preparation of the endometrium as we can see in a typical natural cycle. Around day 14 to 16 is when we have the highest thickness of the endometrium and the endometrium is proliferative. Then later on we have the corpus luteum secreting the progesterone and under progestogenic influence as we can see.
Day 19 to day 24 we have a highly secretory endometrium with tortuous vascularity and glandular openings and this is the environment which is conducive for implantation and here is when the blastocyst enters the uterine cavity, attaches itself to the endometrial epithelial cells, apposes and invades inside, burrows inside and then there is a successful implantation. Among various molecules that are mentioned here interleukin 6, transforming growth factor beta 1 active in A, leukaemia inhibiting factor interleukin 11, there are so many others perhaps even thousands that are responsible for the successful endometrial to embryo dialogue to make sure that the implantation is successful. So here we have the embryo maternal so-called crosstalk at implantation.
There is literally a dialogue by which both the endometrium as well as the embryo secrete autocrine and paracrine factors and there is literally a dialogue that happens which ensures that the embryo reaches the point of the highest implantation potential such that after implantation there is not only successful mutation and invasion of the embryo but also a successful pregnancy throughout the 9 months of gestation. So various molecules mentioned here responsible in signalling that we have various chemokines, leucopins, we have various inhibiting factors, growth factors, some of the important molecules mentioned here are cytokines, growth factors as you can see, even COX-2, LIF etc which are all responsible for this dialogue to happen successfully. So first there is apposition of the embryo, later on there is adhesion and finally there is an invasion inside the endometrial lining.
Again, there are various molecules among whom interleukin-11 and leukaemia inhibiting factor are known to be present in the uterine fluid during the receptive phase. As we can see here the implantation window can shift itself based on what sort of a cycle we have. So in a natural cycle typically as it is depicted by circular as we can see it typically starts on day 18 and under progesterogenic influence which is at peak on day 20 to day 21 is the time of successful implantation and the implantation window is finally shut around day 23.
In a controlled ovarian hyper stimulated cycle on the other hand because of the supraphysiological oestrogen level the implantation window is shifted ahead of its time. So instead of day 18 the window starts opening on day 17 itself and there is a steep rise of oestrogen such that the window is preceded ahead and it shuts down earlier as well. So instead of day 22 or day 23 it shuts down probably a day or two earlier and if we don't do the embryo transfer in this time of the window of implantation we might miss out and we might have a failed implantation and therefore it is often suggested that those patients who respond highly to the ovarian stimulation especially PCOS patients perhaps a frozen embryo transfer is better than a fresh transfer for the same reason that supraphysiological E2 levels would shift implantation ahead of its time.
On the hormone cycle on the other hand for example in a frozen embryo transfer or a recipient cycle as depicted by the line indicating squares it is on the right as we can see the window starts developing a little later perhaps on day 19 and it is shifted to day 21 to day 22 of the point of maximum implantation potential. Again, it is known to shut down at its usual time it is just that we have to remember that in a frozen or a recipient cycle the implantation window is postponed whereas in a fresh embryo transfer with controlled ovarian stimulation the implantation window is pre-poned. 30% embryos are lost to pre-implantation stage so human reproduction is known to be highly inefficient and this is the proof we you know getting specific it is known that the pre-implantation stage itself we have a loss of almost 30% embryos which is quite significant and 30% of the embryos they do implant but then they fail early so we probably can get a positive with diet cg and if we do then we call it a biochemical pregnancy but sometimes the patient does not even know that the embryo had successfully implanted itself all she experiences is perhaps a delayed period by a day or two and she gets a period later.
Human reproduction as we can see 30 plus 30 is almost 60% of all pregnancies are lost before they even become clinically detectable and therefore human reproduction is often cited to be a very inefficient process and almost 10% of all the embryos are lost after the mis period that is once they become detectable clinically and a disturbance in the embryo to maternal dialogue is cited to be a major reason why 60% of all pregnancies are terminated at the end of preimplantation period. So on the one hand we have the successful fertilisation followed by zygote formation we have four cell stage on day two uh eight cell stage on day three boreal on day four then we have an early blastocyst developing blastocyst and late almost implanting hatched blastocyst on day six and on the other hand the endometrium is developing parallelly simultaneously on day 12 to day 14 already there is a peak estrogenic activity the progesterone starts secreting right after ovulation which is day 14 and we have the corpus luteum secreting grammes and grammes of progesterone in the body and by day 20 the progesterone is at the peak level and we have endometrium which is completely secretory and conducive to the incoming embryo and there we have around day 20 which is the peak implantation period this endometrium to embryo dialogue which successfully results in implantation.
If you are looking for a trusted platform to pursue your Fellowship in Reproductive Medicine Program, join Medline Academics - an institute offering hybrid mode of education for all practicing clinicians. Their modules and lectures are clear, practical, and regularly updated to match real-world medical needs. Students also get support from experienced faculty and can attend live sessions and hands-on training. It does not matter whether you have just completed your masters or have experience, Medline Academics is a great place to learn and keep yourself updated.
As a leading IVF hospital in Bangalore, Dr. Kamini Rao Hospitals is dedicated to providing comprehensive care for couples navigating the challenges of infertility. Through its Fellowship in Reproductive Medicine program, the clinic combines current clinical remedies with specialised counselling services to cope with both the bodily and emotional factors of infertility. This holistic approach ensures that sufferers acquire personalised care, fostering desire and resilience on their adventure closer to parenthood. For over 40 years, Padma Shri Prof. Dr. Kamini A Rao has been training 1000+ doctors and helping numerous couples get the joy of having babies.
You may also like
More from this category.

The Power of Tandoor Ovens in Modern Commercial Kitchens
Tooth Extraction in West Delhi – Expert Oral Surgery Care | DentoHub

Vinny Pizza: A Slice of Authentic Flavor with a Modern Twist

County Pizza: Where Local Flavor Meets Legendary Taste
NextGen Diagnostic Imaging

Get the Perfect Smile with the Best Orthodontist in Langar House at FMS Dental

Best Dentist in Hyderabad – Patient-Focused Care at FMS Dental

Why Selenium Is the Most Popular Tool for Web Automation?
Anti-Aging Treatments: Modern Solutions for Youthful, Healthy-Looking Skin

